


| MOQ: | 1kg |
| Price: | US $15/kg |
| Standard Packaging: | Cylinder/Tank |
| Delivery Period: | 15 days |
| Payment Method: | L/C, T/T |
| Supply Capacity: | 5000kg/month |
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gas is a colorless, flammable, and highly toxic gas with a distinct odor of rotten eggs. It occurs naturally in some environments, such as swamps, volcanic gases, and certain industrial processes. Hydrogen sulfide is also produced by the breakdown of organic matter containing sulfur, such as in sewage and manure.
Here are some key points about hydrogen sulfide gas:
Toxicity: Hydrogen sulfide is highly toxic and poses significant health risks. Even low concentrations can cause irritation of the eyes, respiratory system, and mucous membranes. Higher concentrations can lead to more severe symptoms, including headaches, nausea, dizziness, unconsciousness, and even death.
Sources: Hydrogen sulfide can be released from various sources, including industrial processes like petroleum refining, natural gas extraction, and wastewater treatment. It can also be encountered during certain agricultural activities, mining operations, and in confined spaces with poor ventilation.
Detection and Monitoring: Due to its toxic nature, hydrogen sulfide should be carefully monitored in occupational and industrial settings. Gas detectors and monitors are commonly used to measure and alert workers to the presence of hydrogen sulfide in the air.
Safety Precautions: When working in environments where hydrogen sulfide may be present, appropriate safety precautions should be taken. This includes providing adequate ventilation, using personal protective equipment (such as respirators and gas detectors), implementing safety protocols, and training workers on the risks and proper response procedures.
Treatment and First Aid: In cases of hydrogen sulfide exposure, immediate medical attention is crucial. Affected individuals should be removed from the contaminated area and provided with fresh air. If necessary, cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and other life-saving measures may be required.
Due to the toxic nature of hydrogen sulfide gas, it is essential to prioritize safety and follow established guidelines and regulations when working with or around this gas.
| DOT Class | 2.3 & 2.1 | Un No | 1053 |
| Cylinde | DOT/ISO/GB | Cylinder Pressure | 15MPa/20MPa |
| Valve | Cga330 | Melting Point | -85.5 ºC |
| Appearance | Colorless, Rotten Egg Smell | Boiling Point | -60.4 ºC |
| Density | 1.36 Kg/M3 | Molecular Weight | 34.08 |
| Transport Package | 47L, 800L | Specification | 99.5%, 99.9% |
| Trademark | CMC | Origin | China |
| HS Code | 28309090 | Production Capacity | 2000 Tons/Year |
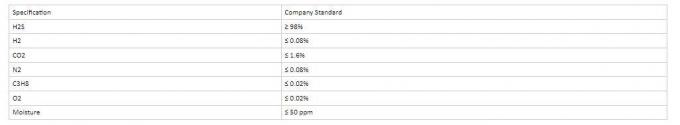
Specification:


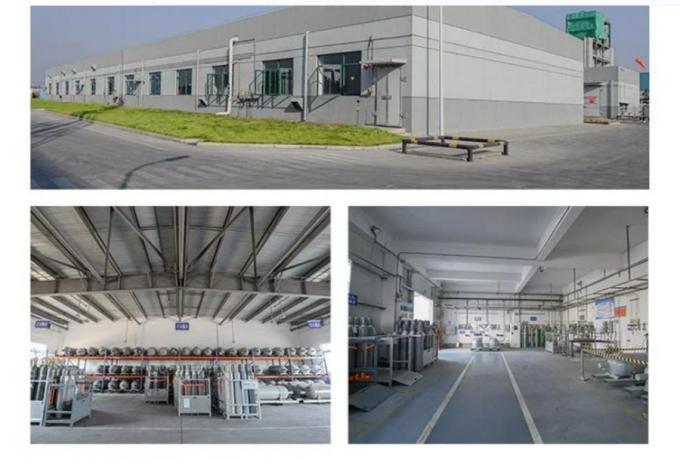
Detailed Photos






| MOQ: | 1kg |
| Price: | US $15/kg |
| Standard Packaging: | Cylinder/Tank |
| Delivery Period: | 15 days |
| Payment Method: | L/C, T/T |
| Supply Capacity: | 5000kg/month |
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gas is a colorless, flammable, and highly toxic gas with a distinct odor of rotten eggs. It occurs naturally in some environments, such as swamps, volcanic gases, and certain industrial processes. Hydrogen sulfide is also produced by the breakdown of organic matter containing sulfur, such as in sewage and manure.
Here are some key points about hydrogen sulfide gas:
Toxicity: Hydrogen sulfide is highly toxic and poses significant health risks. Even low concentrations can cause irritation of the eyes, respiratory system, and mucous membranes. Higher concentrations can lead to more severe symptoms, including headaches, nausea, dizziness, unconsciousness, and even death.
Sources: Hydrogen sulfide can be released from various sources, including industrial processes like petroleum refining, natural gas extraction, and wastewater treatment. It can also be encountered during certain agricultural activities, mining operations, and in confined spaces with poor ventilation.
Detection and Monitoring: Due to its toxic nature, hydrogen sulfide should be carefully monitored in occupational and industrial settings. Gas detectors and monitors are commonly used to measure and alert workers to the presence of hydrogen sulfide in the air.
Safety Precautions: When working in environments where hydrogen sulfide may be present, appropriate safety precautions should be taken. This includes providing adequate ventilation, using personal protective equipment (such as respirators and gas detectors), implementing safety protocols, and training workers on the risks and proper response procedures.
Treatment and First Aid: In cases of hydrogen sulfide exposure, immediate medical attention is crucial. Affected individuals should be removed from the contaminated area and provided with fresh air. If necessary, cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and other life-saving measures may be required.
Due to the toxic nature of hydrogen sulfide gas, it is essential to prioritize safety and follow established guidelines and regulations when working with or around this gas.
| DOT Class | 2.3 & 2.1 | Un No | 1053 |
| Cylinde | DOT/ISO/GB | Cylinder Pressure | 15MPa/20MPa |
| Valve | Cga330 | Melting Point | -85.5 ºC |
| Appearance | Colorless, Rotten Egg Smell | Boiling Point | -60.4 ºC |
| Density | 1.36 Kg/M3 | Molecular Weight | 34.08 |
| Transport Package | 47L, 800L | Specification | 99.5%, 99.9% |
| Trademark | CMC | Origin | China |
| HS Code | 28309090 | Production Capacity | 2000 Tons/Year |
Specification:



Detailed Photos





